Wolff rearrangement

The Wolff rearrangement is an organic reaction used to convert an α-diazo ketone to a ketene using a silver oxide catalyst, light, or thermal conditions. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement is essentially one step which is initiated by the catalyst. The reaction involves a 1,2-shift to form the ketene product and release a molecule of nitrogen gas. Subsequent attacks by nucleophiles to the ketene formed are also considered Wolff rearrangement. [1]
Mechanism
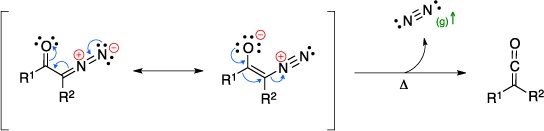
References:
| 1. |
Wolff, L.; Krüche, R.
Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem.
1912,
394,
23–59.
|